Some installers/customers may comment on excessive
engine coolant consumption, or an engine coolant leak near or under the
throttle body area of the upper intake manifold. This could be related to upper intake manifold composite material
that may degrade around the EGR stove pipe and could result in an
internal or external coolant leak.
To make the repair, follow the upper intake manifold removal
instructions found in the Engine Unit Repair section of the service
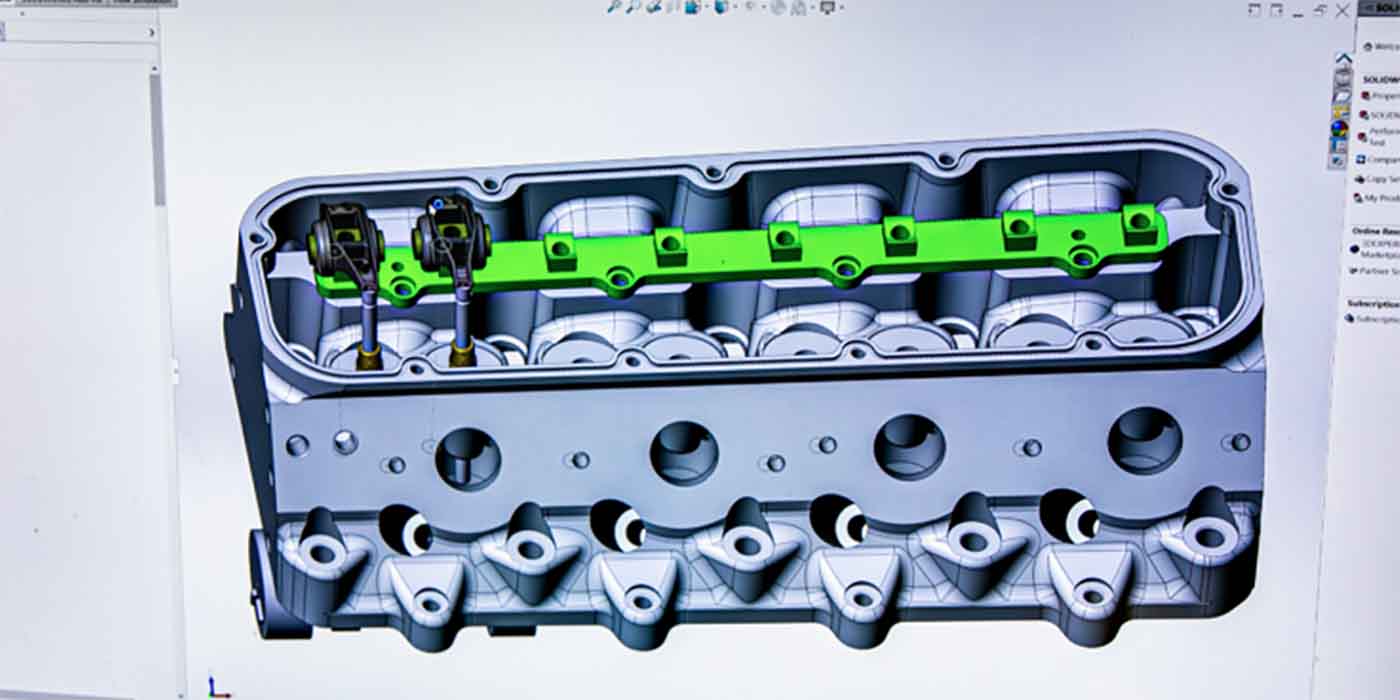
information manual. Refer to the arrow in the illustration of the upper intake manifold (see Figure 1).
Inspect the inner diameter of the EGR passage for signs of material
degradation. Degradation will appear as “pitting” of the composite
material in the EGR port passage. If degradation of upper intake manifold composite material is found,
replace the lower and upper intake manifolds with the following part
numbers:
Part Number Description
89017554 Gasket Kit, Upper Intake Manifold
89017272 Manifold Kit, Upper Intake
89017400 Gasket, Lower Intake Manifold
24508923 Manifold, Lower Intake
Follow the lower and upper intake manifold installation
instructions found in the appropriate
service manual. If degradation is not apparent, installers should evaluate the vehicle for other
causes of excessive coolant consumption as noted in the service manual.
You should discard the previous
GM Bulletin Number 01-06-01-007B (Section 06 – Engine).
Some or all of this information was provided by the Automotive
Parts Remanufacturers Association (APRA). For more information on
technical bulletins available through APRA call 703-968-2772 or visit www.AutoBulletins.com.