Neglected oil change intervals can ruin the best engine oils. As engine oil accumulates miles, it becomes contaminated with carbon, water and various acids, all of which are a by-product of internal combustion and which will form a film of black, gooey sludge on the interior parts of the engine.
Auto manufacturers, in general, are continuing to reduce vehicle maintenance requirements by extending oil change intervals.
However, many vehicle owners are forgetting to check their engine’s oil level between oil changes.
The most common result is an engine ruined by excess accumulations of varnish and sludge due to using motor oils that are not approved by the engine manufacturer. In less common instances, the engine fails due to low engine oil levels and a subsequent lack of lubrication.
Whatever the case, extended oil change intervals are changing how we should recommend and perform scheduled vehicle maintenances.
[inpost_gallery post_id=4852 group=”1″]
Oil DEPOSIT CONTROL
While lead-free, high-detergent gasoline has dramatically reduced intake port and combustion chamber deposits, modern engine oils are also specially formulated to prevent carbon from forming in the combustion chamber, piston rings from sticking and oil additives from contaminating the catalytic converter.
In particular, modern engines generally use narrow, low-tension piston rings that are fitted very tightly into the piston to increase piston ring sealing and reduce oil consumption.
On the upside, low piston ring tension reduces rotating friction and cylinder wear. On the downside, low-tension rings with tight side-gap clearances tend to stick when the incorrect engine oil is used. Therefore, the ability of an engine oil to clean and lubricate the piston ring package is critical.
ANTI-SCUFFING ADDITIVES
Oil suppliers have also eliminated zinc and phosphorous-based anti-scuff additives that reduce catalytic converter efficiency. While the elimination of these particular anti-scuff additives has increased camshaft wear on some high-performance pushrod-style engines, it hasn’t affected overhead camshaft engines due to the lower valve spring pressures used on overhead camshaft designs.
On the other hand, some engines equipped with direct fuel injection require a high degree of anti-scuff protection to prevent the camshaft-driven high-pressure fuel pump and camshaft lobe from wearing out. In most cases, oil refiners have gone to much higher quality base oils to prevent wear on the high-pressure fuel pump and cam lobe. Again, it’s vitally important to make sure that the replacement oil is either OE oil or is approved by the OE manufacturer.
As for older, performance pushrod, flat-tappet engines that are not equipped with catalytic converters, specially branded performance oils are available with anti-scuff additives to prevent camshaft and valve lifter wear. In addition, zinc-based “ZDDP” additives are also available to enhance the anti-scuff qualities of over-the-counter motor oils. Again, these oils and additives are not intended for vehicles equipped with catalytic converters.
OIL LIFE ISSUES
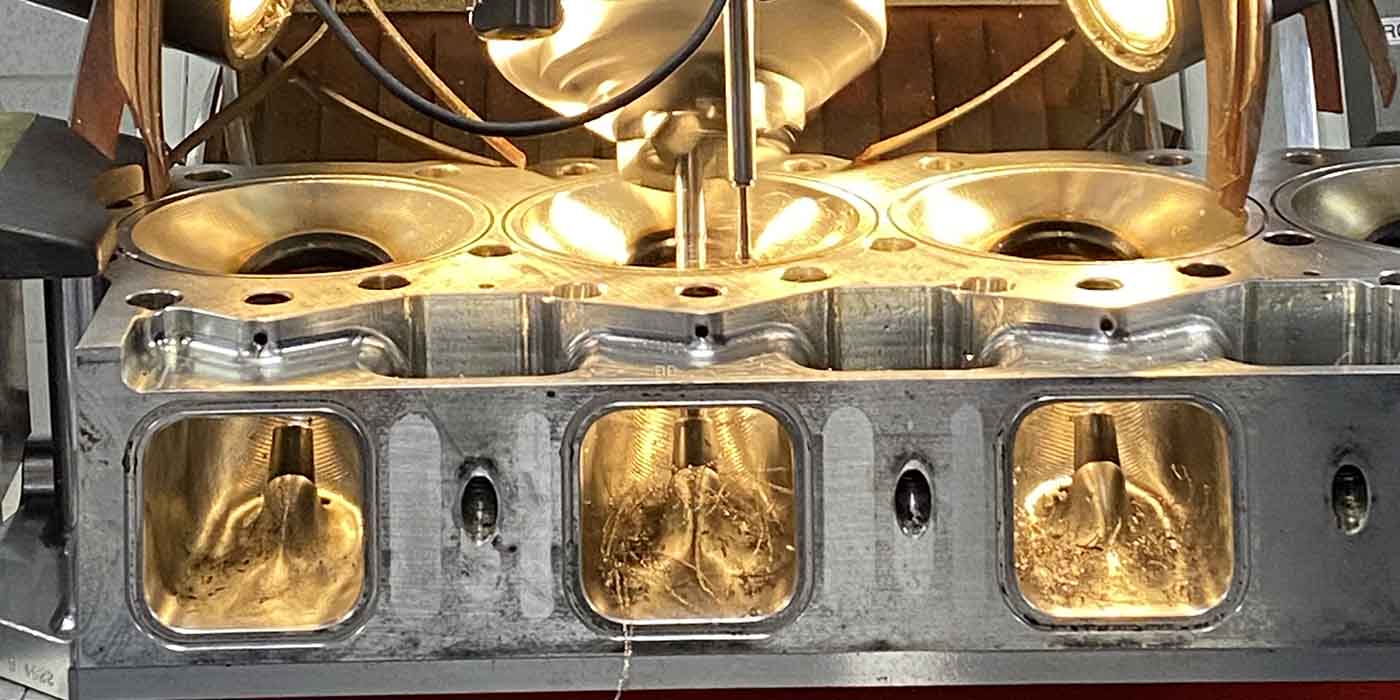
Neglected oil change intervals can ruin the best engine oils. As engine oil accumulates miles, it becomes contaminated with carbon, water and various acids, all of which are a by-product of internal combustion and which will form a film of black, gooey sludge on the interior parts of the engine.
Cold-engine operation accelerates the formation of sludge because the oil temperatures aren’t sufficient to evaporate accumulated moisture. Oil sludging is also aggravated by short-trip, cold-weather driving and by thermostats that are stuck open. See Photo 1.
ENGINE LUBRICATION PROBLEMS
When the engine is operated at high speeds and temperatures, sludge often dislodges and clogs the oil filter. Since most oil filters incorporate bypass valves that allow the lubricating oil to flow around a clogged filter media, the dirty oil can pass directly into the engine and clog small-diameter oil galleries.
In any case, heavily sludged oil will eventually clog the engine’s oil pump pickup screen, oil filter and oil galleries. The initial symptoms of oil starvation are engines that become noisy during cold start-up and oil pressure gauges that rise very slowly.
Broken timing belts are also symptomatic of oil starvation on overhead camshafts. Because the damage usually includes the crankshaft and piston assemblies, don’t be too eager to quote a cylinder head replacement as the cure for a seized camshaft. See Photo 2.