During our research of the General Motors Gen III engine family we continued to run up against a stumbling block of exterior identification between the 4.8L and 5.3L engines. It seemed that no matter who we spoke with, be it core suppliers, wrecking yards, engineers or rebuilders, when asked how they differentiated between the 4.8L or 5.3L engine from the exterior, no one had a solid answer. As a matter of fact no one had any answer.
So we thought we would look at the internal component differences between these two engines and perhaps come to some solution of external identification.

These engines came on the scene in 1999 in General Motors truck applications and were the upcoming replacement for the original design small block engines (GenIE). They were a spinoff of the LS1, 5.7L passenger applications used in the Corvette, Camaro and Firebird two years prior. Just so we have all the ducks in a row, both of these engines are OHV, pushrod V8 engines with cast iron blocks and aluminum cylinder heads.
Because both engines use the same block (c/n 12551358), GM seemed to play what may be described as a cruel, twisted joke on us since it cast "4.8/5.3" right on the block both in the front and in the rear in large numbers. The only problem is that you never really know which engine that you have from the exterior. The standard cylinder bore for both engine applications is 96mm (3.779˝) however the stroke for the 4.8L is 83mm (3.268˝) and has a crankshaft casting number of 12553482 while the stroke for the 53L is 92mm (3.622˝) and that crankshaft casting number is 12552216. Looking at the two crankshafts just standing next to each other they do not have what you would consider an obvious difference in appearance.
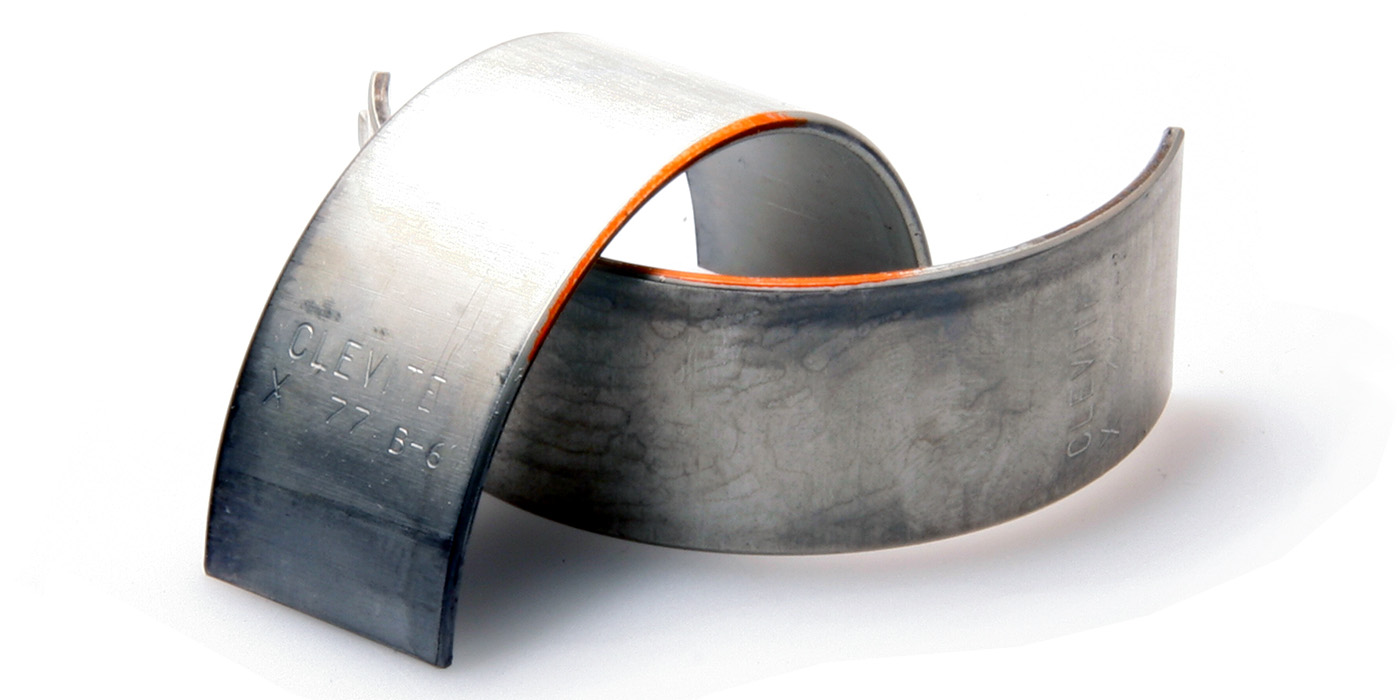
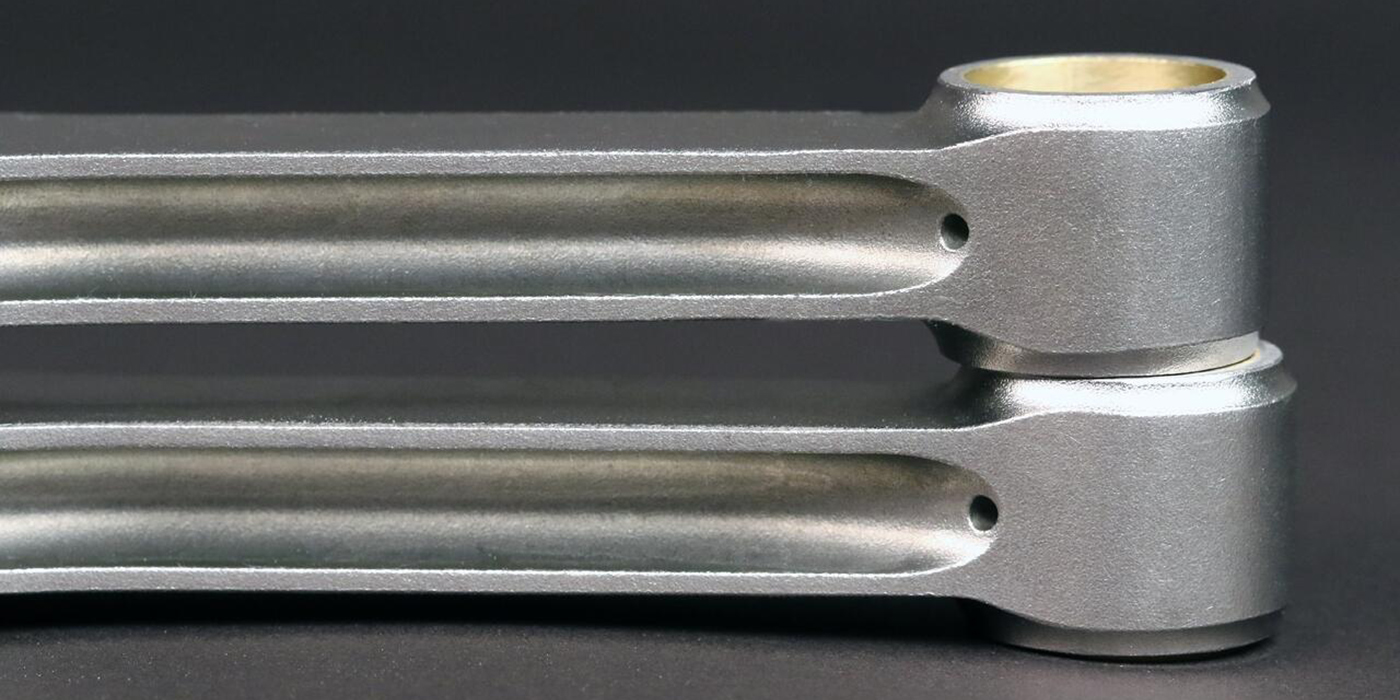
The connecting rods for the two engines do provide us some visual identifiable differences. The 4.8L connecting rod is longer in length and has the casting number 121 with an additional boss on the thrust face. The 5.3L connecting rod is shorter with casting number 143 and no additional boss on the thrust face. Both connecting rods are PM (powder metal) with a "crack" parting face.
There is also a difference between the pistons of these two engines, the 4.8L has a flat dome and the 5.3L has a cup dome. Another thing that we noticed is that the 4.8L pistons from OE had a pink ink mark in the pin area and the 5.3L had a green mark.

The cylinder head for both engines is aluminum with a casting number of 862, however on the deck face area in a small cavity there is a 4.8 cast onto the cylinder head. Do not be confused by this cast number for the cylinder head is for both 4.8L and 5.3L engines.
So how does any of this help with our ability to discern between these two engines from the exterior? If the oil pan is off, you could look at the crankshaft casting number, only every time you want to do that your odds are about as good as an open face peanut butter and jelly bread hitting the floor face up. But you can look at the connecting rods and see if that additional boss is there, you have eight chances to do that! But do you really want to pull the oil pan if you don