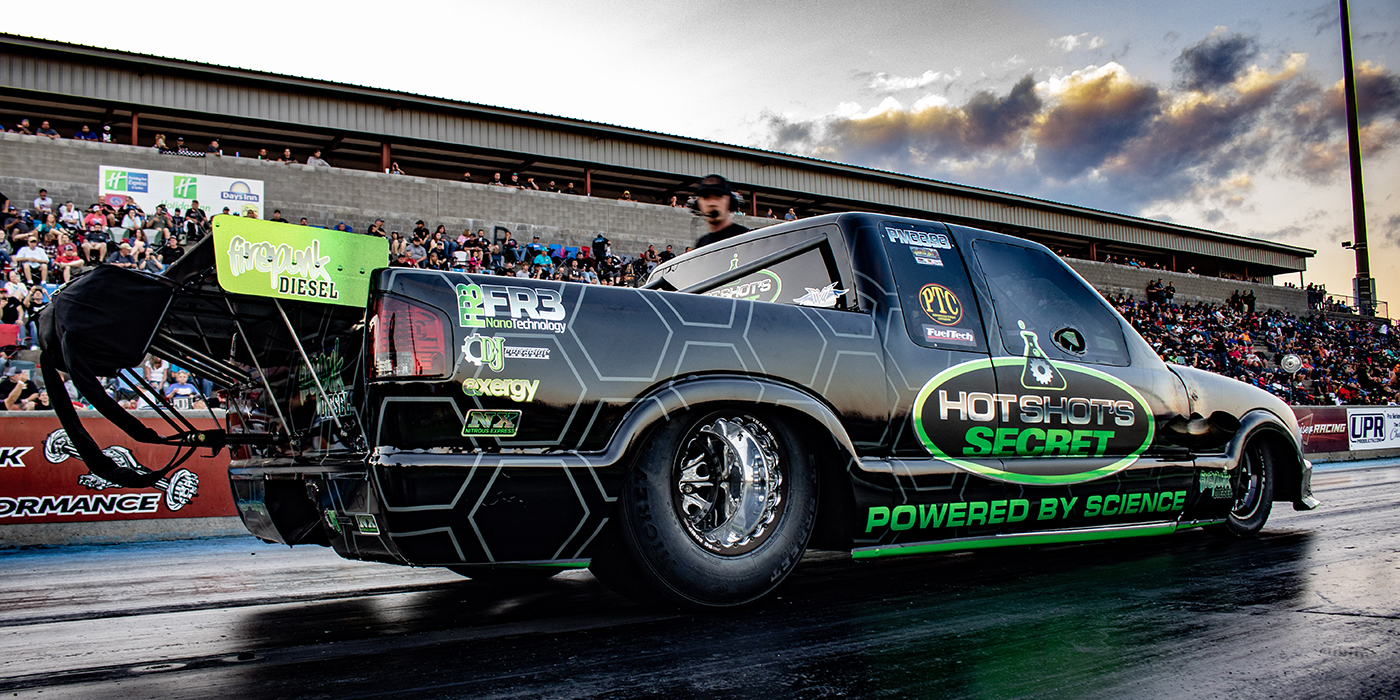
The diesel engine market has been rapidly changing in recent years. Higher fuel prices and changes in emission regulations have brought about a whole new generation of clean diesel engines in both the light and heavy-duty truck markets.
According to the Diesel Technology Forum (www.dieselforum.org), particulate emissions from new on-highway diesel engines have been reduced 83 percent since 1988. Nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions are down 83 percent over the same time period. With the latest low sulfur diesel fuel and exhaust particulate traps, diesel emissions will be reduced up to 90 percent.
 Because of their higher fuel efficiency (typically 20 to 40 percent better than a gasoline engine with the same displacement), diesel engines power most heavy-duty trucks, transit buses and emergency vehicles. Diesel engines power most farm machinery as well as a majority of school buses and medium-duty trucks. Diesel engines are also a popular option in many pickup trucks. But Volkswagen has been the only vehicle manufacturer to sell diesel-powered cars in the U.S. in recent years, and in 2007 they didn’t offer any because of changes in diesel emission regulations.
Because of their higher fuel efficiency (typically 20 to 40 percent better than a gasoline engine with the same displacement), diesel engines power most heavy-duty trucks, transit buses and emergency vehicles. Diesel engines power most farm machinery as well as a majority of school buses and medium-duty trucks. Diesel engines are also a popular option in many pickup trucks. But Volkswagen has been the only vehicle manufacturer to sell diesel-powered cars in the U.S. in recent years, and in 2007 they didn’t offer any because of changes in diesel emission regulations.
In Europe where fuel prices are considerably higher than in the U.S., and emission regulations are more diesel-friendly, 50 to 60 percent of passenger cars are now powered by diesel engines. Many experts predict that the number of diesel-powered passenger cars in the U.S. will increase dramatically over the next few years as auto makers introduce a new generation of clean diesel-powered cars that meet the new emission rules – especially if fuel prices remain high. That means more diesel-engine rebuilding opportunities down the road.
The interest in diesel performance has also been growing. Bolt-on performance packages for diesel-powered pickup trucks can easily add 75 to 150 horsepower or more for everyday driving and towing. Pulling has been a traditional event for diesel-powered tractors and trucks, but diesel-powered vehicles are now winning races and setting records in venues that have long been the exclusive realm of gasoline-powered engines.
 A diesel-powered Audi race car recently won the Le Mans 24 hour endurance race in France. A new land speed record of 328 mph was set by the diesel-powered JCB Dieselmax streamliner at Bonneville a little over a year ago. Back in 2002, Gale Banks set a speed record of 217 mph in a Cummins diesel-powered Dodge Dakota pickup truck at Bonneville.
A diesel-powered Audi race car recently won the Le Mans 24 hour endurance race in France. A new land speed record of 328 mph was set by the diesel-powered JCB Dieselmax streamliner at Bonneville a little over a year ago. Back in 2002, Gale Banks set a speed record of 217 mph in a Cummins diesel-powered Dodge Dakota pickup truck at Bonneville.
A group called the Diesel Hot Rod Association (www.dhraonline.com) has been promoting diesel drag racing at various tracks around the country. Many of the diesel-powered Pro Street trucks at these events are running in the 9-second range at speeds in excess of 140 mph in the quarter mile. The fastest diesel pickup truck is currently a twin turbocharged 6.6L Duramax-powered Chevy S10 built by Gale Banks. Last October, the S10 set the record by covering the quarter mile in 8.21 seconds at 165 mph. We’re also seeing more diesel-powered rail dragsters with modified Cummins or Duramax engines.
 The point is there’s a lot of interest lately in making diesels go fast. Because of this, a number of aftermarket engine parts suppliers are looking at light truck diesels as a growth opportunity for new performance products (including pistons). And as new diesel performance parts become more available (and affordable), it will create new engine building opportunities for many of our readers.
The point is there’s a lot of interest lately in making diesels go fast. Because of this, a number of aftermarket engine parts suppliers are looking at light truck diesels as a growth opportunity for new performance products (including pistons). And as new diesel performance parts become more available (and affordable), it will create new engine building opportunities for many of our readers.
The Diesel Difference
The most obvious difference between a gasoline-powered engine and a diesel is that a diesel has no spark plugs or ignition system. The fuel is ignited by the heat of compression alone. When a diesel piston goes down on its intake stroke, it only draws air into the cylinder. When the piston comes up on its compression stroke, the fuel is injected into a precombustion chamber or directly into the combustion chamber by a high pressure injector (1,500 psi to as much as 27,500 psi depending on the system). The injection pulse is actually a series of pulses timed to provide maximum power and lowest possible emissions. Residual heat in the cylinder from the last combustion cycle combined with heat generated by compression ignites the fuel.