This information supersedes the previous technical bulletin, dated March 25, 2005. The previous bulletin should be removed from your files. This bulletin applies to vehicles equipped with a 2.4L engine built between February 1, 2004 and April 5, 2005.
Whenever re-torquing the cylinder head bolt(s), be sure to follow the torque sequence as outlined below. If there are no external signs of damage to any parts, attempt the procedure below before replacing a cylinder head, cylinder head bolts or cylinder head gasket.
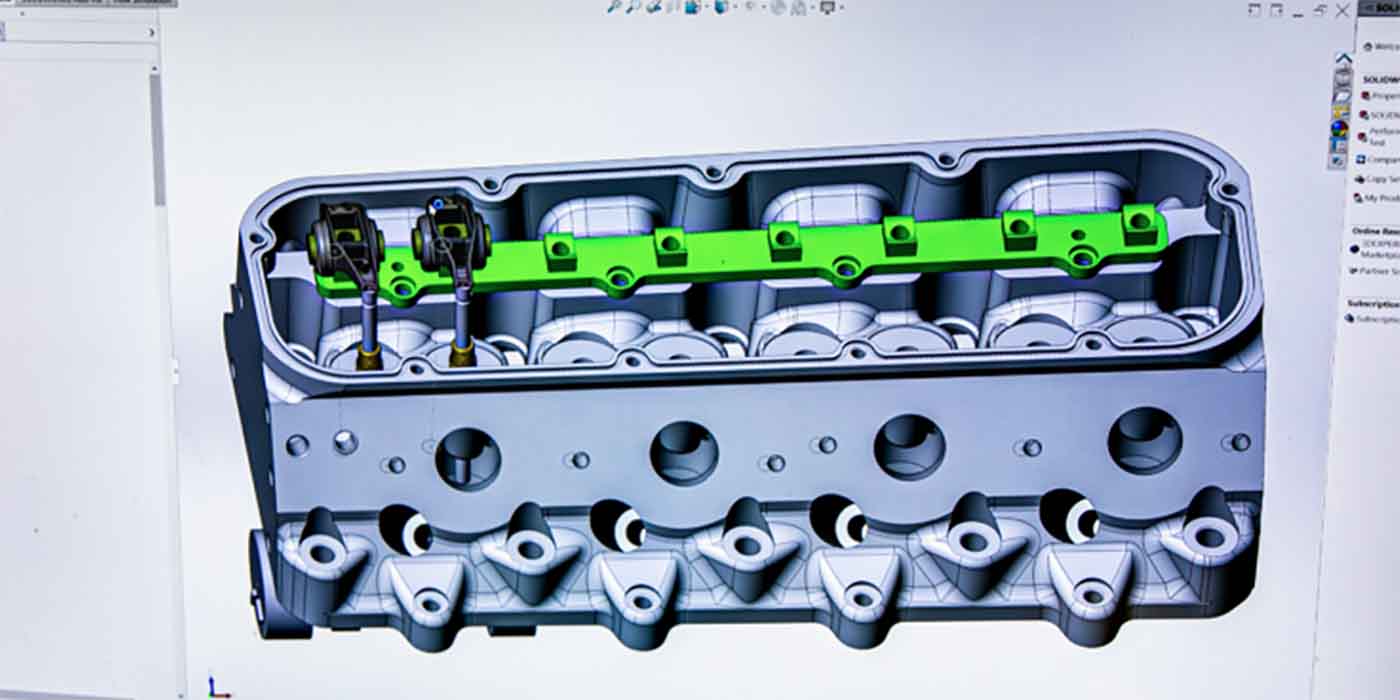
1) Using a six inch wobble plus extension friction ball and shallow socket following the torque sequence (Fig. 1), loosen one bolt at a time to 0 torque and then torque that same head bolt to 60 Ft-lbs.
2) Repeat step 4 for every head bolt one bolt at a time in sequence.
3) Verify that each head bolt is at 60 Ft-lbs before performing next steps.
4) After all head bolts have been verified to be torqued to 60 Ft-lbs , follow the torque sequence and turn the head bolts an additional 90° (1/4 turn) (Fig. 1).
5) Following the appropriate procedures to install the cylinder head cover.
Some or all of the technical information was provided by the Automotive Parts Remanufacturers Association (APRA). For more information on technical bulletins available through APRA call 703-968-2772 or visit www.AutoBulletins.com.