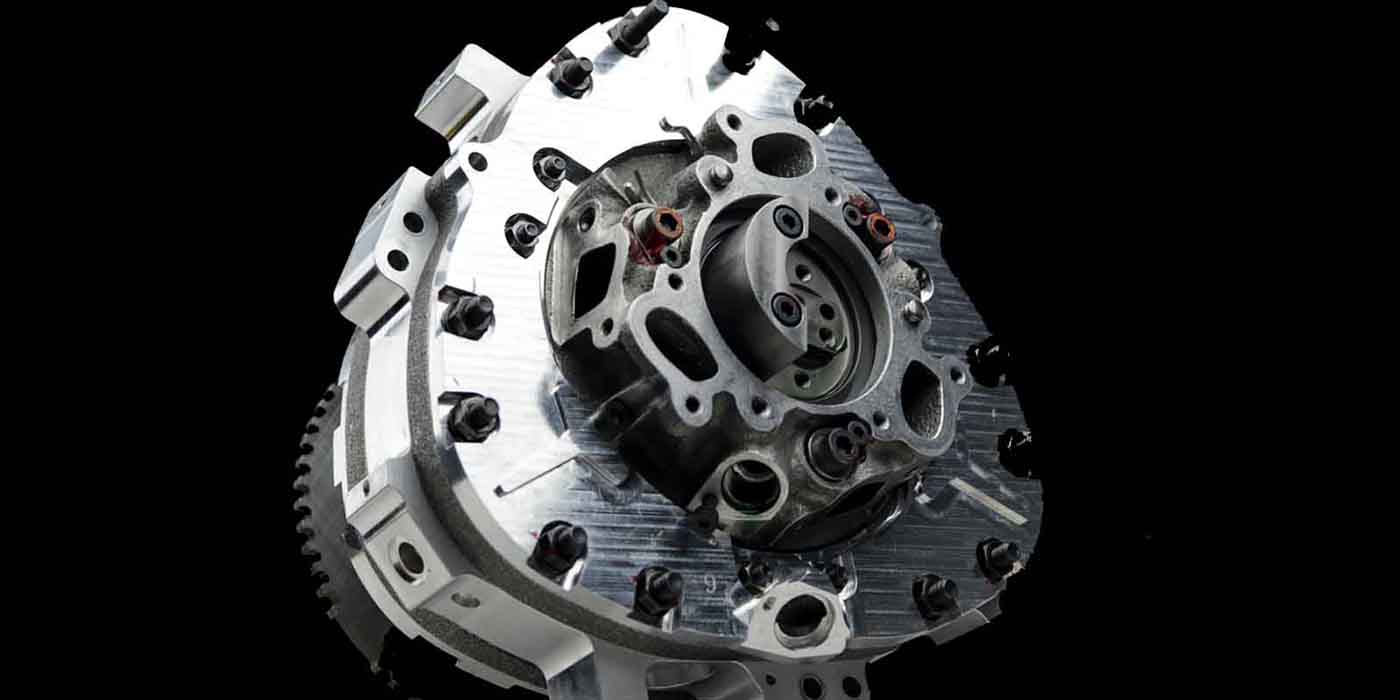
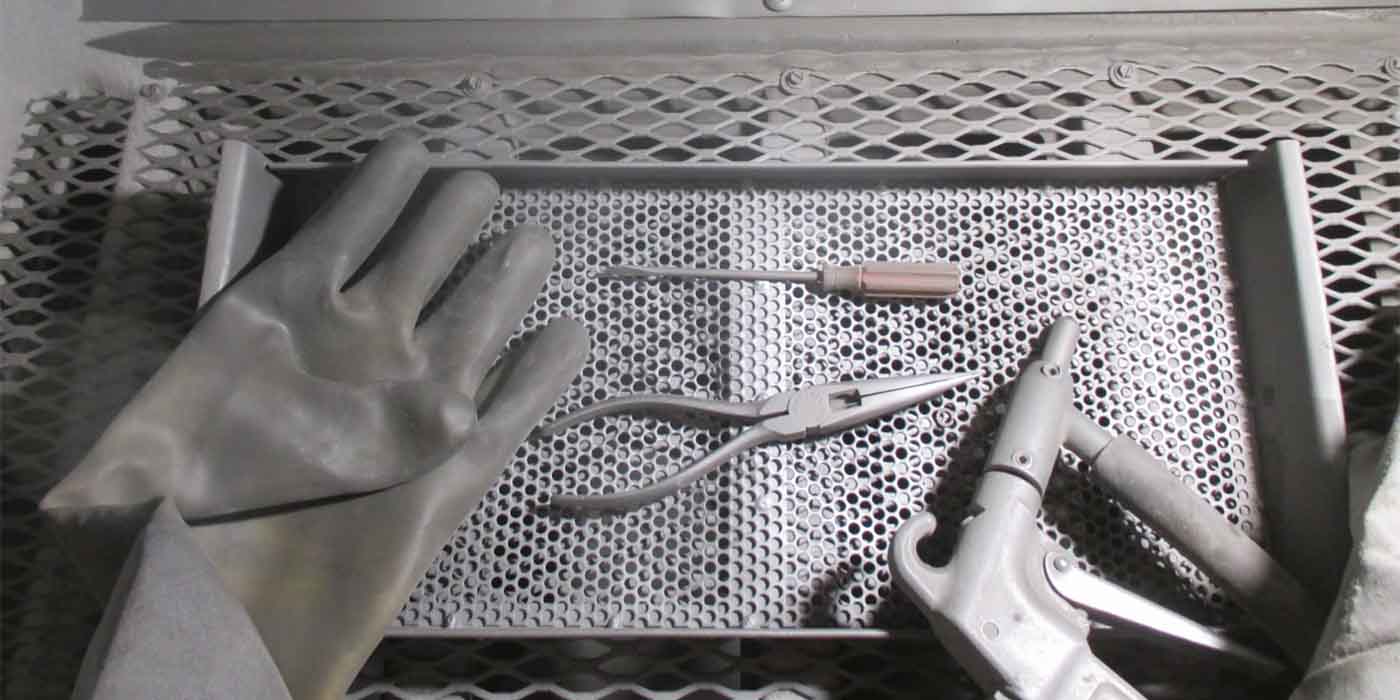
Verify the leak by looking at the end of the crankshaft (Figure 1). If oil is present in the bore (where the torque converter nose engages the crankshaft), a special
service procedure should be performed. If the bore is dry, or oil appears to be
from the seal area, perform normal oil leak analysis. A service cup plug has
been developed to stop leakage that may occur in this area (p/n WPC-340).
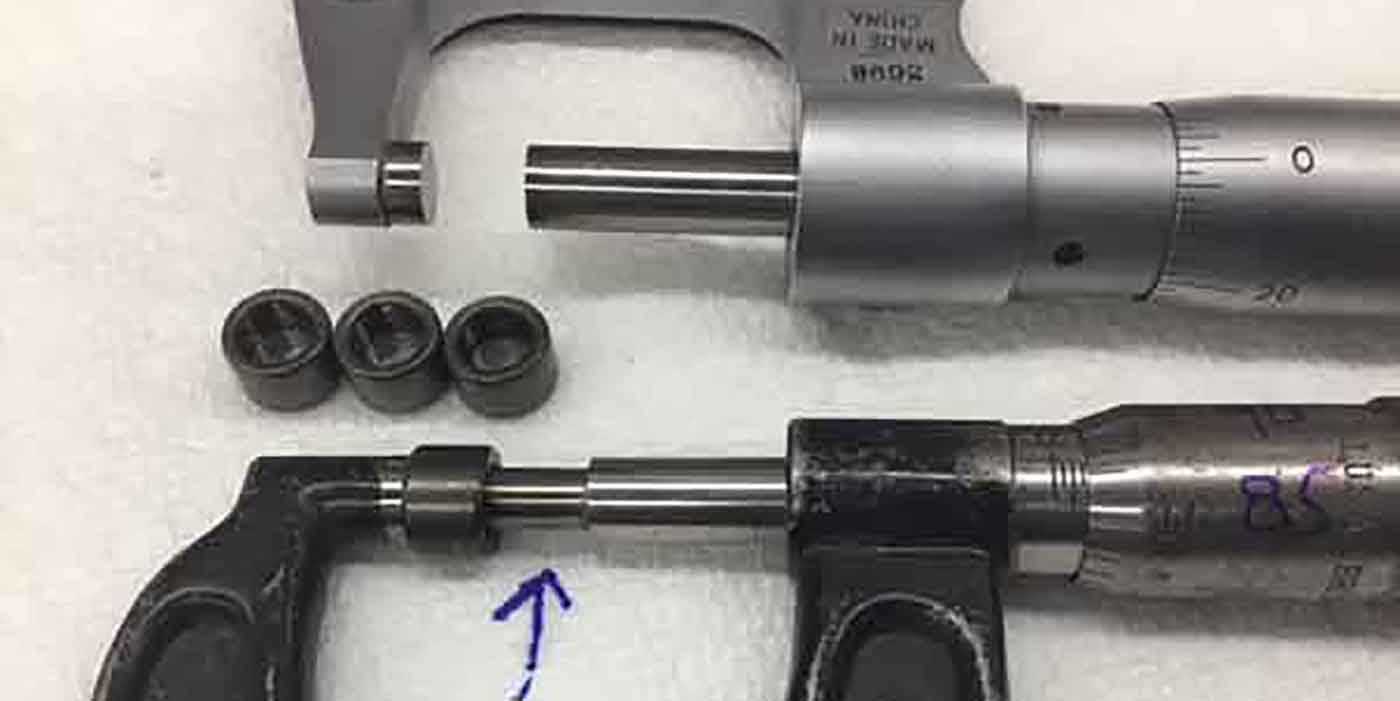
Note: General Motors offers a tool to aid the installation. If the tool is not
available through your local dealership, an aftermarket equivalent is acceptable (Figure 2).
Clean the crankshaft flange bore area with brake clean or equivalent.
Thoroughly dry the area and examine the bore surface for irregularities. If the
bore surface needs additional cleaning, use sand paper or equivalent and clean
as necessary. Once the crankshaft bore is clean and smooth, apply a thin bead
of Loctitite™ 620 completely around the inside of the crankshaft flange bore.
Position the crankshaft service cup plug into the crankshaft flange bore with
the service cup plug, dish side outward (Figure 3). Note: Do not use the
impact socket with hammer to drive the service cup plug into place. Damage to
the crankshaft thrust bearing may occur.
Assemble arbor, forcing screw, attaching bolts and socket. Install the tool
press assembly to the end of the crankshaft flange and position the socket and
service cup plug into the bore of the crankshaft flange. Be sure you have the
proper tool set up before pressing the cup plug into the end of the crankshaft.
The forcing screw will fit inside an 18 mm or 19 mm end of the impact style
socket with the 1/2" drive side of the socket facing the service cup plug.
The forcing screw should bottom on the 15 mm step inside the socket (Figure 4).
Hand tighten forcing screw into the socket, making sure that it is centered on
the service cup plug. Mark forcing screw and arbor for reference, then tighten
forcing screw two complete turns and an additional 90 degrees or 1/4 turn more (Figure 5).
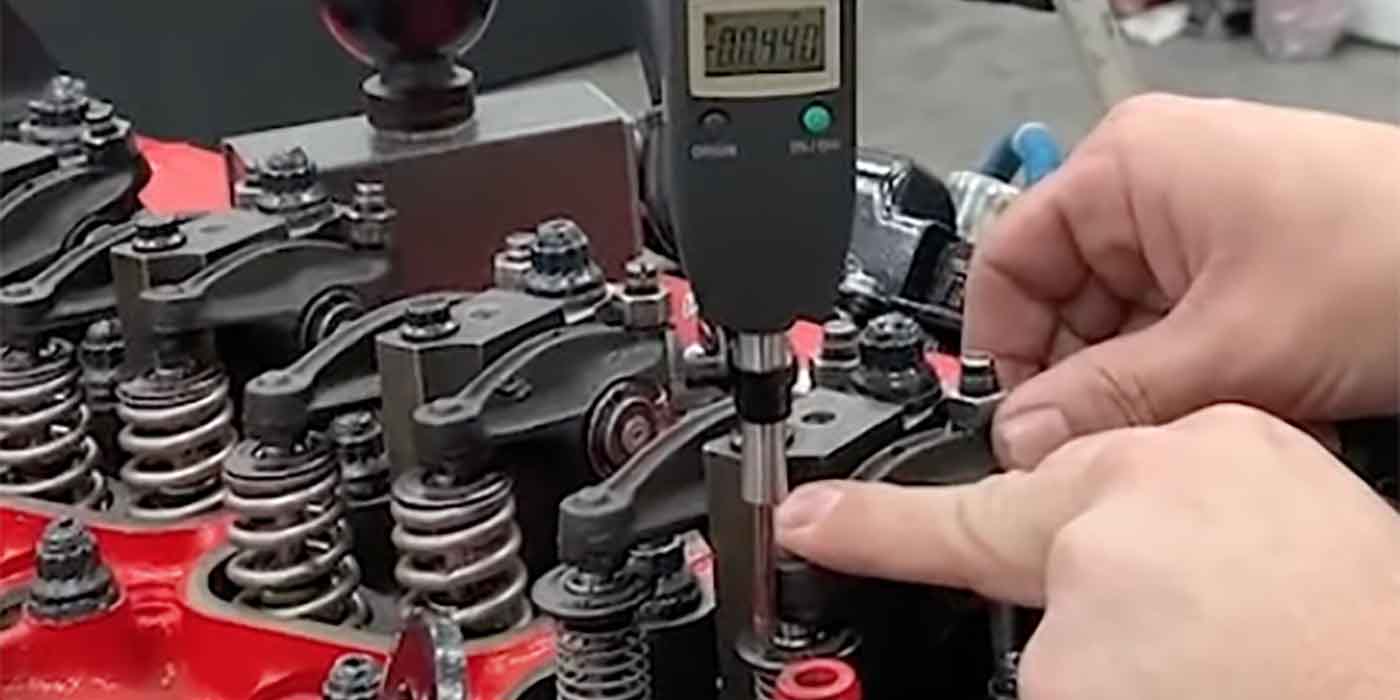
When completed, remove installation tool assembly and confirm the installation
depth of the service cup plug. Place a straight edge across the center of the
crankshaft flange as the measurement point. Measure from the straight edge to
the center of the installed cup plug (Figure 6). The depth of the installed cup plug
should be 16-17 mm (.630"-.670").
Some or all of this information was provided by the Automotive
Parts Remanufacturers Association (APRA). For more information on
technical bulletins available through APRA call 703-968-2772 or visit www.AutoBulletins.com.