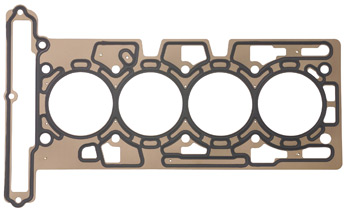
Cylinder head gasket design has become more sophisticated than in years past. The following FAQs on head gaskets may give you a better understanding of WHY you need to rebuild a particular engine.
Can an overheating motor cause a head gasket failure?
One reason head gaskets fail is because of engine overheating. If the engine gets too hot, the cylinder head can swell to the point where it crushes the head gasket (usually between the cylinders because this is the thinnest point).
The extruded material and/or cracked combustion armor then provides a leak path for coolant and/or combustion gases.
Can head bolts be reused?
Bolt breakage and uneven gasket loading or loss of torque can cause a newly installed head gasket to leak. TTY head bolts are designed for one-time use because they stretch permanently once they are torqued down. This helps even out the clamping force of the cylinder head on the head gasket.
But if the bolts are reused, stretching them even farther greatly increases the risk of the bolt breaking.
Some replacement head gaskets come with new TTY head bolts, but others do not. If the bolts are not included, they should be included as an add-on sale. Many customers may not realize they should not reuse TTY head bolts. If an engine has conventional head bolts, it’s okay to reuse them — provided the bolts are in good condition and the bolts are not stretched.
Bolts can be cleaned, then lightly oiled and reused. Dirty or damaged threads, or failing to lubricate the bolts before they are installed, can cause false torque readings when the bolts are tightened, which may allow the head gasket to leak.
Can engine knock cause a head gasket to fail?
Another reason head gaskets fail is because of damage caused by detonation (spark knock). Detonation causes a sharp spike in combustion chamber pressure, which, over time, can overload and crack the gasket armor that surrounds the cylinder.
This leads to burn through and loss of compression. Detonation can be caused by a variety of problems. One is an accumulation of carbon in the combustion chamber that increases compression. Many late-model engines run fairly high compression ratios, and some require premium octane fuel. If compression reaches a point where the fuel ignites spontaneously before the spark can set it off, the engine will knock and ping under load.
Why are some vehicles more prone to head gasket failures?
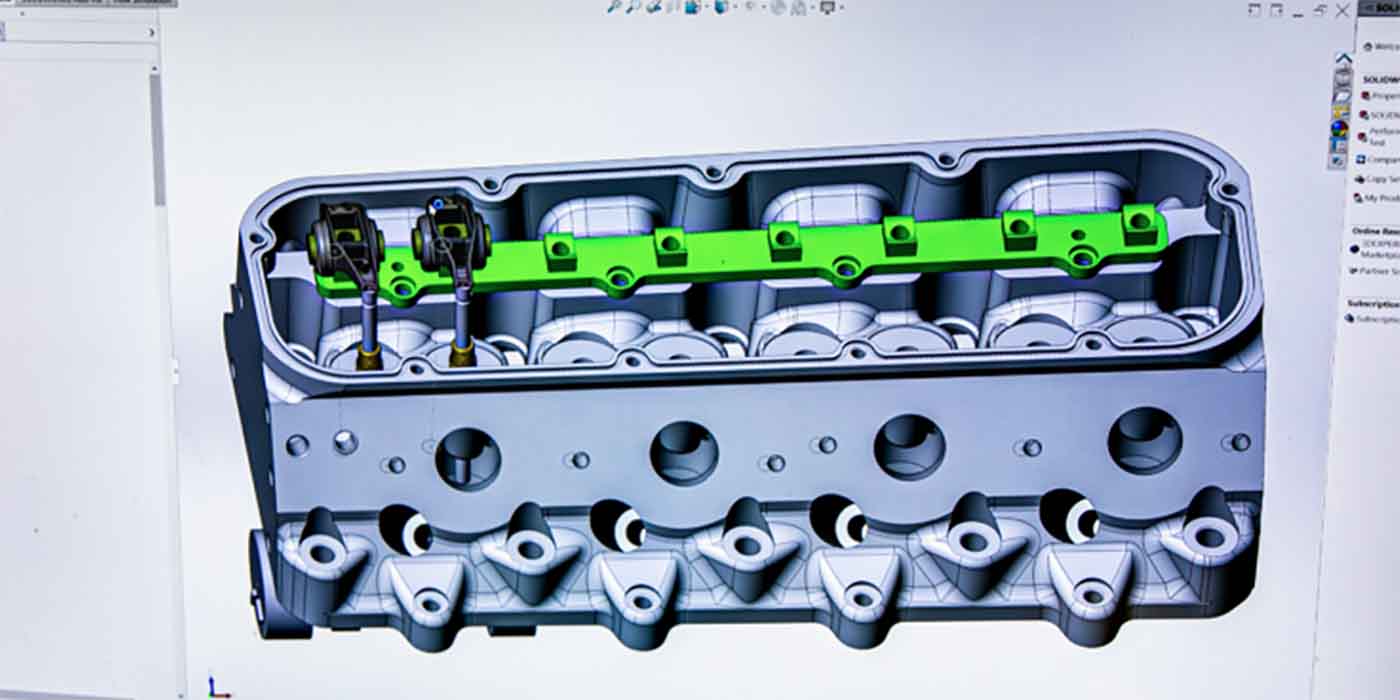
Sealing problems are inherent in bi-metallic engines because aluminum cylinder heads expand faster than cast-iron cylinder blocks during the warm-up cycle. The difference in expansion rates is further aggravated because the cylinder head tends to heat up much faster than the cylinder block.
The difference in expansion rates between aluminum and cast iron creates a “scrubbing” effect that eventually wears out the stainless steel “fire ring” that keeps combustion gases from entering the cooling system. Because the cumulative effect of these repeated thermal events results in failed cylinder head gaskets, most aftermarket gasket manufacturers have designed head gaskets using space-age materials that resist scuffing wear in bi-metallic applications.
Can a leak only occur during warm-up?
Yes. Temperature-related failure patterns are the most common. As always, the primary symptom of a leaking head gasket is increased consumption of coolant with no apparently visible external coolant leakage.
If cylinder leakage occurs during cold-engine operation, combustion gases accumulate under the engine’s thermostat during cold engine operation, forcing the coolant back through the radiator and resulting in an overflow condition at the coolant reservoir. If, on the other hand, leakage occurs only under full throttle, hot engine operation, the coolant may become aerated with combustion gases, which reduces cooling system efficiency and increases operating temperatures.
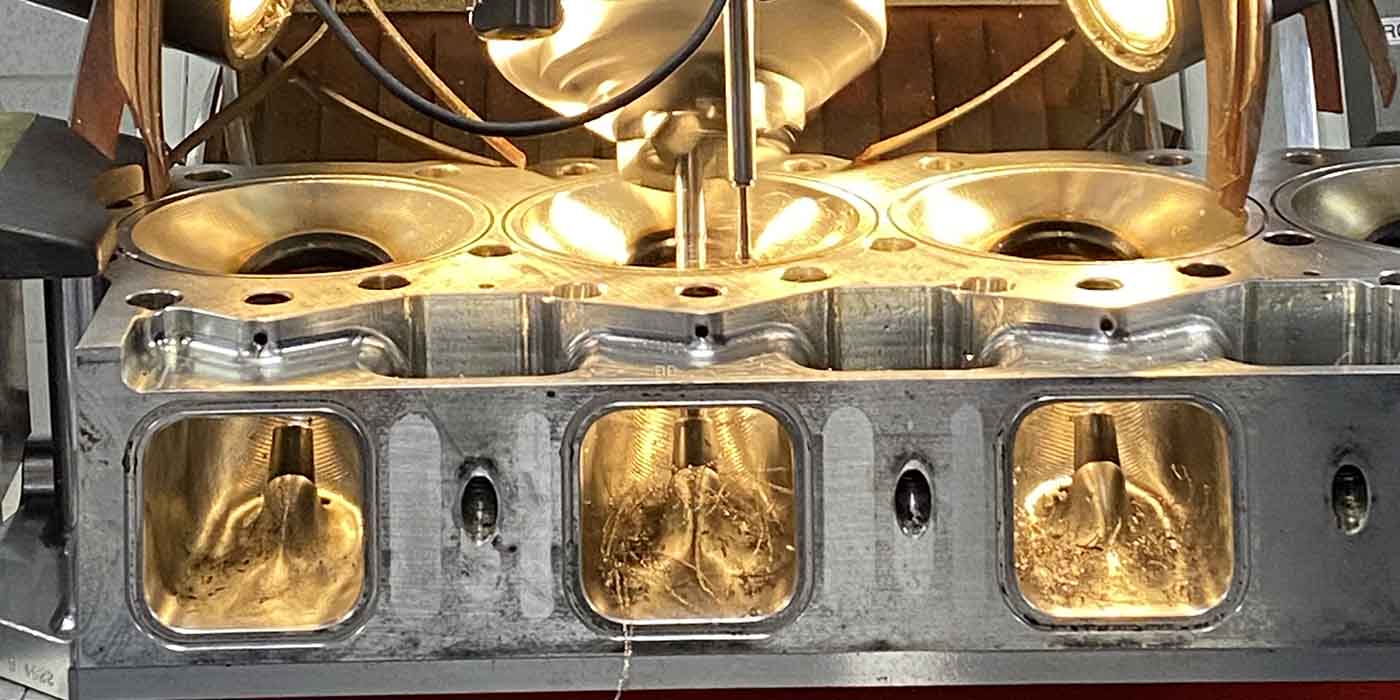
What determines the gasket surface of the head and block?
The level of surface finish is determined not only by the engine materials, but the gasket type. The aluminum cylinder head surface should be resurfaced to the cylinder head gasket manufacturer’s specifications.
In short, the head gasket surface should appear polished rather than rough, with composite gaskets requiring a finish of no more than 45 roughness average (RA) and MLS gaskets a finish of 20-30 RA. The rougher the surface on an aluminum cylinder head, the shorter the cylinder head gasket life.