With the landscape of automotive power-trains continuing to evolve, one contender whose future looks as uncertain as ever is the Wankel or rotary design. But uncertain as its future may be, the prospects of the Wankel might have just improved. It seems Mazda has yet to give up on the rotary engine, according to recent comments from their CEO, Masamichi Kogai.
With the landscape of automotive power-trains continuing to evolve, one contender whose future looks as uncertain as ever is the Wankel or rotary design. But uncertain as its future may be, the prospects of the Wankel might have just improved. It seems Mazda has yet to give up on the rotary engine, according to recent comments from their CEO, Masamichi Kogai.
In remarks to Autocar at the Frankfurt Auto Show, Kogai reiterated that Mazda was continuing to develop the rotary design for use in the modern marketplace. Included on the roster are 30 engineers from Mazda, partnered with universities around the world. Kogai’s remarks join scattered rumors and comments from the Japanese automaker about a possible return of the RX nameplate.
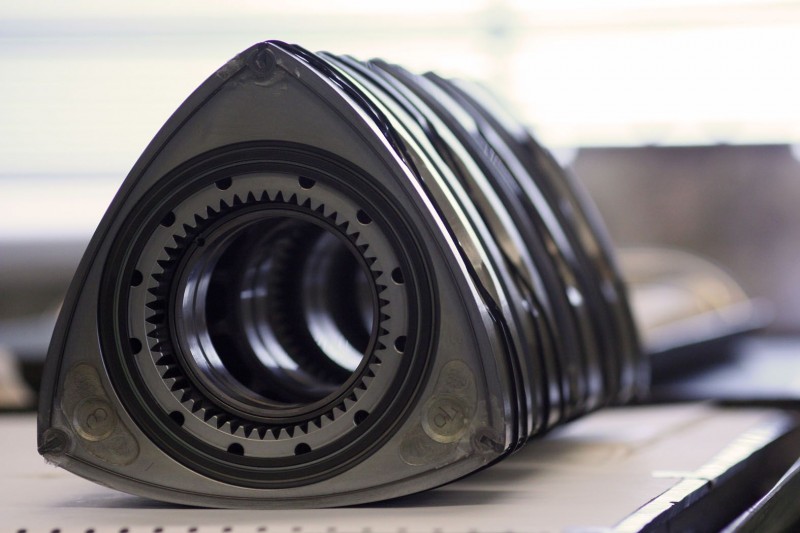
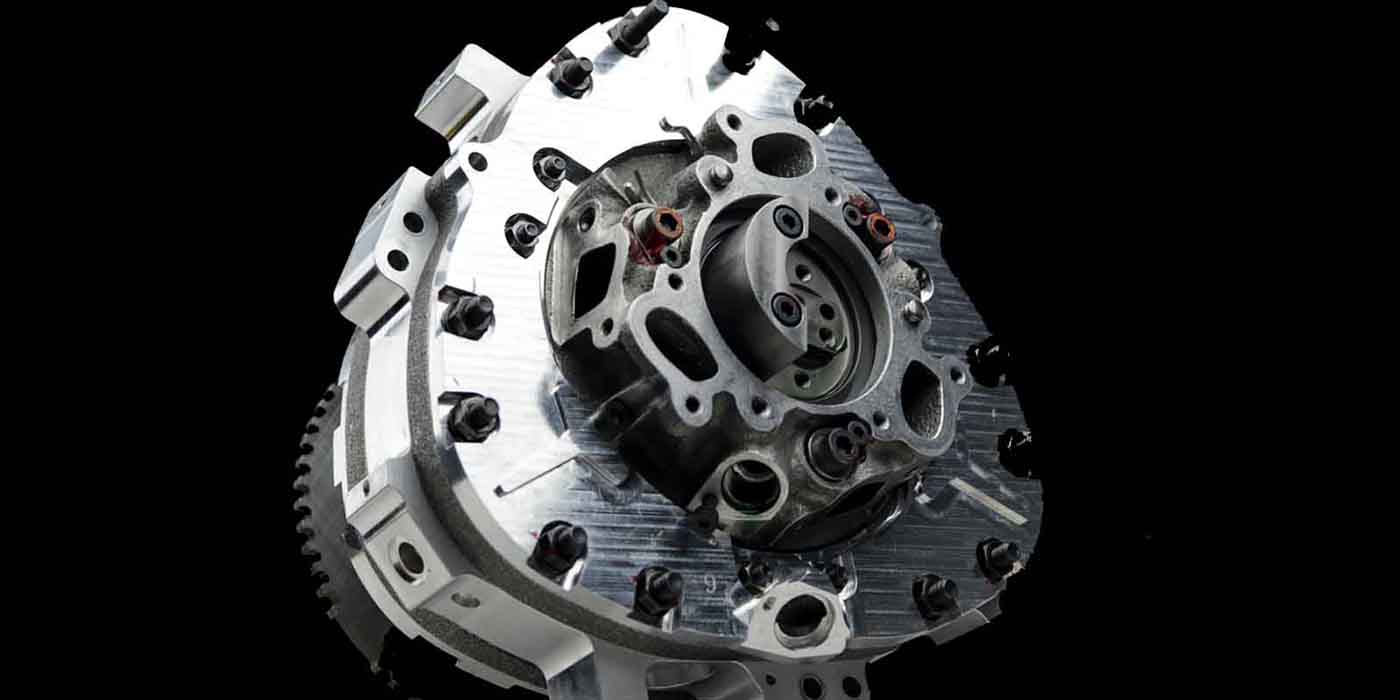
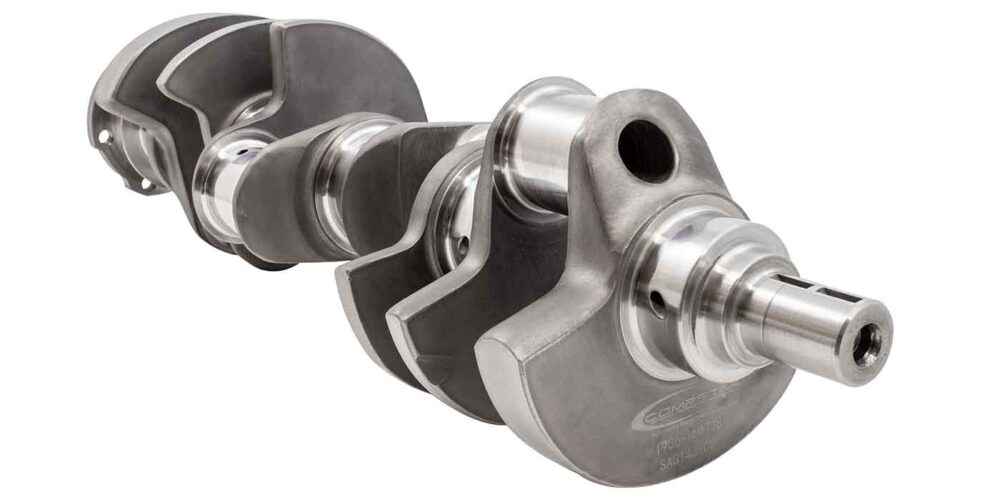
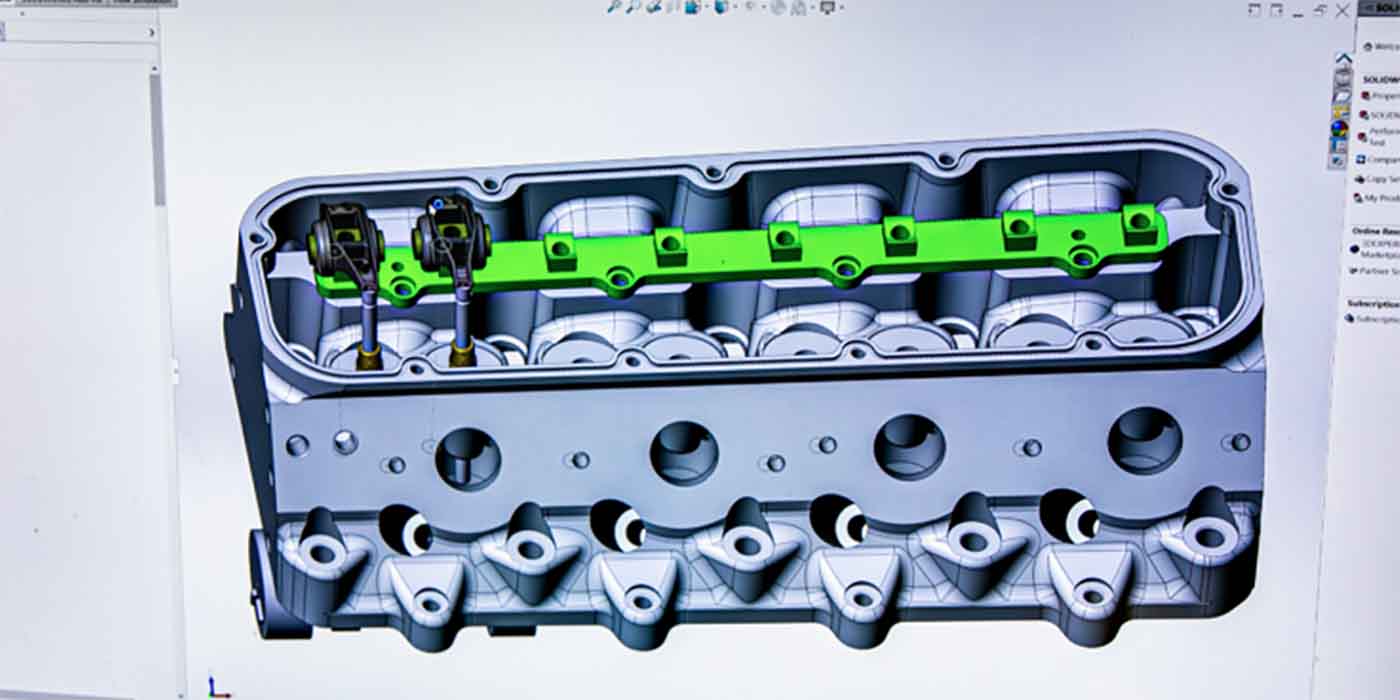
The RX-8 was the last of a long line of models marketed under the RX nameplate, which sported rotary power; the RX-8 succeeded the RX-7, which ran from 1978 until 2002. The 1.3 liter two rotor engine that powered the RX-8, named the Renesis, produced 250 horsepower and was named Engine of the Year in 2003.
Only time will tell what Mazda has in store for the rotary engine. It will probably be a question of whether the demand will support the production and development of a new engine design. In 2004, the first year for the RX-8, the model sold almost 24,000 units but suffered a clear and pronounced decline in the following years, with sales below 1,000 model units in 2012, which ultimately became the last year of production.
 Mazda did unveil a 1.6 liter rotary engine in 2007, called the 16X, that was rumored to be in development for a new model, but this project hasn’t received much publicity since then. One of the more common problems with rotary engines tends to be their difficulty meeting emissions standards, as fuel consumption is typically poor, resulting in the products of incomplete combustion and excess fuel being eliminated by way of the exhaust. Mazda’s last generation of rotary engines, which ceased production in 2012, also heard complaints of poor torque numbers, among cries of poor fuel efficiency; Mazda’s primary point of concern lies in improving the design so that it can meet modern emissions standards. Kogai remarked that Mazda was working “very enthusiastically” to address some of the shortfalls of the rotary engine in contrast to conventional piston engines.
Mazda did unveil a 1.6 liter rotary engine in 2007, called the 16X, that was rumored to be in development for a new model, but this project hasn’t received much publicity since then. One of the more common problems with rotary engines tends to be their difficulty meeting emissions standards, as fuel consumption is typically poor, resulting in the products of incomplete combustion and excess fuel being eliminated by way of the exhaust. Mazda’s last generation of rotary engines, which ceased production in 2012, also heard complaints of poor torque numbers, among cries of poor fuel efficiency; Mazda’s primary point of concern lies in improving the design so that it can meet modern emissions standards. Kogai remarked that Mazda was working “very enthusiastically” to address some of the shortfalls of the rotary engine in contrast to conventional piston engines.
Despite its flaws, the rotary engine provides several advantages over reciprocating piston engines. In addition to achieving higher rpm ranges and better power-to-weight ratings, rotary engines tend to run smoother and without vibration or balance issues, scarcely needing balance shafts or counterweights to the degree their reciprocating cousins do. In concept, rotary engines also deliver greater reliability ratings across the board, due to the idea that the simplest two rotor designs have only three main moving parts- two rotors and an output shaft.
In addition to a revival of the RX nameplate, Mazda has also reportedly considered the use of rotary power-trains as a range extender for electric or hybrid vehicles.