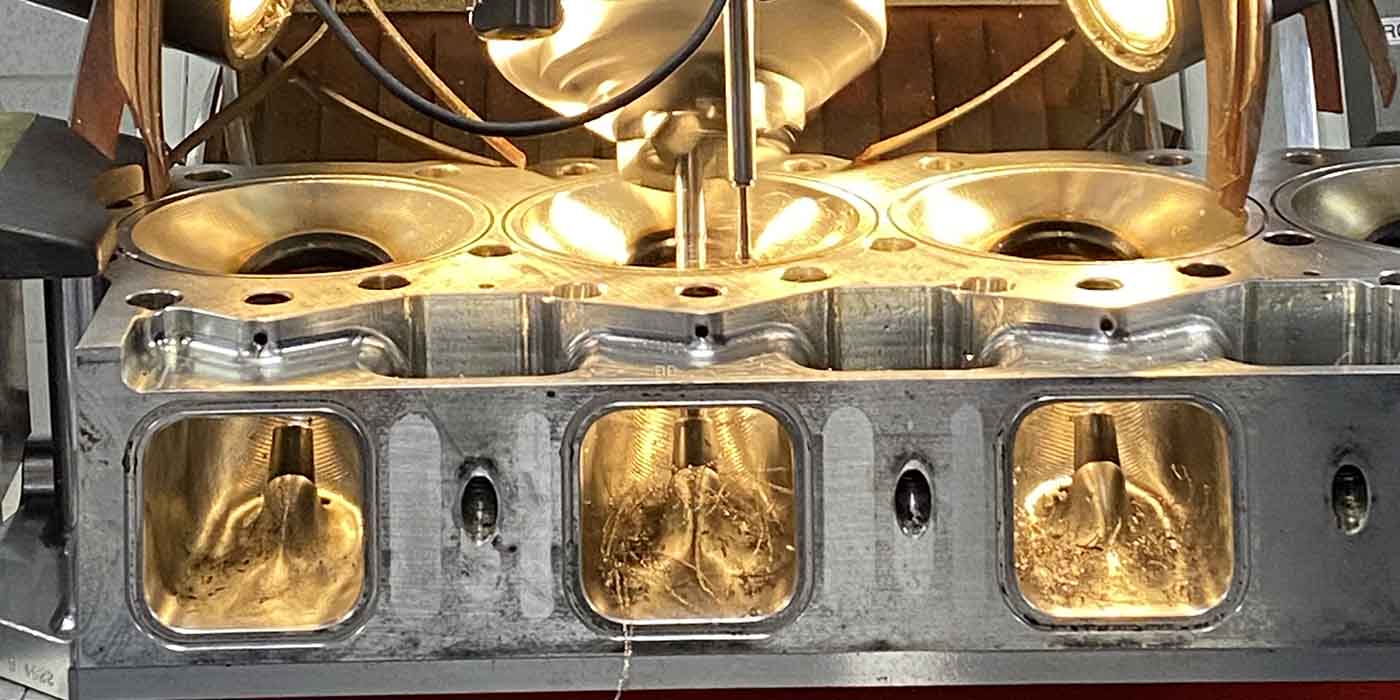
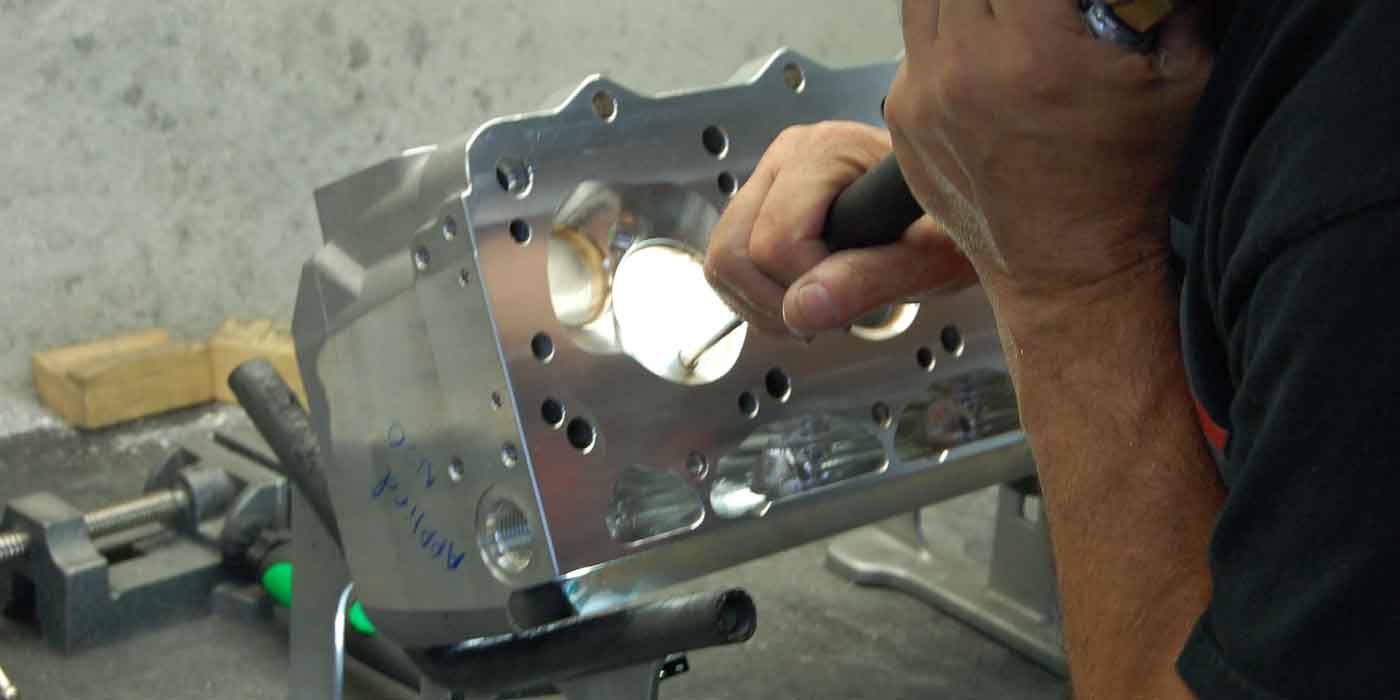
Use a more gentle approach when grinding valve seats. You may have asked this before when working on multi-valve cylinder heads: "What is happening to my valve seats? I’ve tried everything! A new stone, stone holder, pilot and even a new dressing diamond but I can’t achieve seat alignment."
The problem lies more on technique and the power source than in the tooling. Although it’s probably not time for a complete "overhaul" of your equipment and technique, you may need to re-evaluate and make a few changes in the way you’re used to doing things. This is probably one of the easiest and least costly changes you can make to your shop.
Today’s new heads are "dimensionally challenged." Smaller valves require smaller pilots. The pilot area that aligns the newer heads are almost always one half to one third the diameter of its predecessors. This small pilot size allows more deflection, throwing our work off-center. In the past, you may have unknowingly relied on your large diameter pilots for support but pilots are meant for alignment only.
Remember these tips:
1. Be gentle! Don’t push or crowd the valve seats. These smaller seats cannot be bullied like you’re used to doing on the larger cylinder heads. Work must be kept closer to your body, do not work at arm’s length. You’ll have much more control over tooling while reducing deflection and fatigue.
2. Eliminate side pressure. Use a sturdy head stand, an ultralight air hose and light-weight, straight grinder (such as Goodson’s AG-4500). The weight is evenly distributed over the seat. Using an angle grinder motor for your power source is cumbersome and off-center. Since you are grinding valve seats on-center, you should drive the seat grinding tooling on-center as well.
3. Use a free-cutting stone. Using Nickel-Chrome valve seat wheels for small valves virtually eliminate the need to push or crowd the valve seat.
–Tech Tip courtesy of Goodson Tools