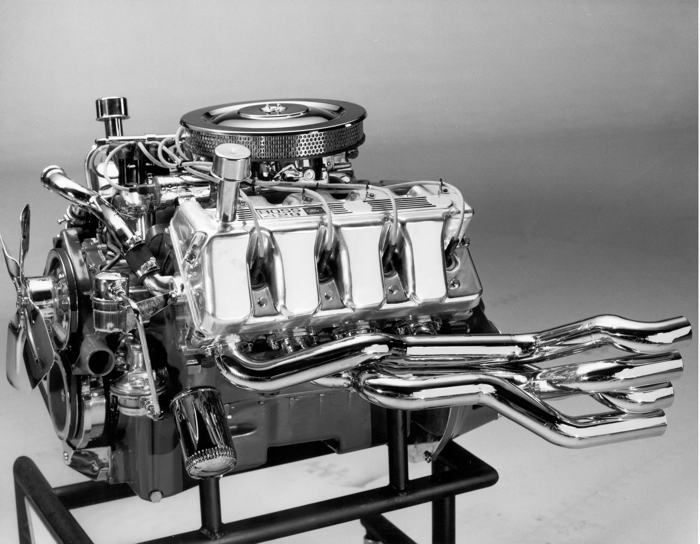
NASCAR’s longtime Labor Day event, the Southern 500, is back home at Darlington (SC) Raceway this year, complete with throwback ‘70s and ‘80s paint jobs to celebrate its rich history. The entire race weekend has become the retro event of the year for NASCAR and Ford Performance talked about race engines with none other than Robert Yates. Yates goes back to those times, building engines at the famed Holman and Moody shops, Ford’s arm for racing. They talked about the engines used in those late-‘60s – early-‘70s days of raging cubic inch wars and fast climbing speeds. For Ford motors back then, it was all about the Boss 429. The iconic engine was created to kill the new 426 Chrysler Hemi and quickly got the nickname of the ‘Shotgun.’
Robert Yates started working at Holman-Moody in 1967 shortly after Ford won the 24 Hours of Le Mans for the second straight year. His main responsibility at the time was to get all of the parts prepped and ready for the 30 engine builders on staff. He worked his way up the ladder and a couple of years later, ended up being part of a group that was challenged to develop and get the Boss 429 ready to race. Yates recalls, “They (Ford) wanted a hemispherical engine like Chrysler’s and they wanted to make it better, and they wanted to leapfrog them if they could. I’d say they did a really good job. We got the engine and the first runs were really about 580 horsepower, which is what the (427) tunnel ports were making. They put four of us on that engine and eight of us on that same engine in another area and said, ‘You’ve got to make these things run better,’ so we got to go work on them. We ended up working on the cylinder heads, doing a lot of flow work, making the ports much smaller. We made our own pistons for it there at the shop and a longer connecting rod and we ended up picking the thing up to 620 horsepower. We picked it up about 50 horsepower after averaging it out, but it was a dry sump.” Yates went on to say, “It was one of the nicest laid out engines I’ve ever seen to this day.”
When asked just what he did to make them faster, he replied, “We changed the port considerably but every engine made 610 horsepower and if you pushed it a little bit and tuned it, you would get about 620, so it was a big improvement.”
It was an intense and all-consuming project with an unusual approach for its development. Yates remembers exactly how much time he spent on the Boss 429, “I was in there working on it 100 hours a week through 1969 and all we knew was that we had to make that thing run better than the tunnel port, so they put two competitive groups together within Holman-Moody to try and make it run better. I’m happy to say I was on the side that accomplished most of it, but we had a really good group of four. We had Bill Roper, Lee Willyard, Denny Woodle and me, and between the four of us we were able to do some things to it. We got a lot of arguments from engineering and it got heated at times. When someone said it wouldn’t work, we had to figure out why. You had to really think through and understand what would happen when you put a longer connecting rod in, and it really made us understand. That was fun being a part of what I consider the most famous engine ever. I learned so much about engines working on that project that it helped me a long ways towards the things I did after that. I think that was the best laid out race engine that’s ever been raced, and that includes what’s running today.”

Just how did that two-group duel work? “There were two development groups. I was in a group of four and Lee Terry led a group of eight and we had a lot of competition. That made it work, too. We’d go to lunch and were plotting on how to kick their butt. John Holman understood competition. If he just had one development deal, it would have been a little lazy, I think. Our group won because we were on it and we had the right people. Everybody was contributing. There wasn’t a leader that told everybody what to do. It worked well because we were all open-minded to it and we had the skills covered. We could make anything. We could do anything. They had access to have anything made, but in our group we could make a piston or a connecting rod. We built the stuff, so we could make changes quicker than a lot of them would even think you could, and that’s what made our deal so good. We had all the skills covered in four guys while the other side had eight, plus the run of the shop. It was fun and it was good competition. We had the best talents there. Our mission was to go and get it done. I believe most of that work was done under Jack Sullivan and he was a lot of inspiration to us. He’d say, ‘Don’t tell me you can’t do it. Do it.’ He was over the engine shop at that time and he gave us anything we needed to make it happen.”
As with any development engine, it was never just one thing that needed work. Yates remembers, “The first connecting rods we broke the caps. We were breaking bolts right and left and got that corrected. I worked night and day changing and putting a different cap on the connecting rod, so we learned, but when you were doing that you had all the factory-backed engines in cars and that was racing. We were like, ‘what are we gonna work on tonight?’ We didn’t wait. We just did it. I know what’s in that engine and I know how we came about it, but that was the nicest stuff I’ve ever worked with on an engine.”
The big HP jumps of those days gone by have now been replaced with finding one lone HP. Yates explains how it is today, “They have a celebration every time they find half a horsepower. We had plenty of room and we just had to understand what it needed. We couldn’t bring it out with it making the same thing the tunnel port made. It just didn’t make sense to bring out the same engine because we knew the Hemis were probably making 590 or close to 600 and when we came out with that Boss engine we kicked their butt. We beat them in power. We beat them in weight. That engine was probably 100 pounds lighter at least. The Hemi was probably 700 pounds and the Boss was 600, so they (Ford) paid attention to weight. They had magnesium oil pans (as well as valve covers) on it and it was still an iron block, but it was well designed. It was a beautiful engine and the thing we wanted to do more than anything was beat the Chrysler.”

Robert Yates has left his car owner days behind but he hasn’t gotten out of building race engines. He’s owned Robert Yates Racing Engines in North Carolina for the past five years and employs a handful of people who work on servicing engines in the NASCAR Whelen Modified Division and K&N Pro Series.
Ford’s current NASCAR engine is the FR-9 and asking Yates about the differences illustrates just how far these engines have come. “The components are half the weight or probably close to half the weight,” says the Champion team owner. “The crankshaft then was 115-120 pounds and it’s 35-40 pounds now, so they’ve reduced all of the rotating weight by half and they’ve reduced all the valves and all the moving components – the rocker arms and the valves themselves are much smaller and much lighter. They’ve reduced all the weights and they’re capable of turning 10,000 vs. 8,000, so 20-25% more RPM with half the weight produce 900 horsepower instead of 600.”
Dave Simon, Ford Performance Motorsports Powertrain Supervisor, played a role in the development of the FR-9 engine used in NASCAR today. He worked alongside Robert’s son, Doug Yates and his staff to bring the engine from concept to reality for the 2010 NASCAR Sprint Cup Series season. Simon discussed how race engines have developed from the Boss 429 to today’s model, “When you look at the Boss 429 before things transitioned to the 351-based engine in 1974-75 and ask the question, ‘What was different about engines then versus the FR9 or current generation NASCAR engines?’ From an architecture standpoint, they’re still two-valve, single camshaft, push-rod, iron block, aluminum head engines. That main configuration or architecture has literally not changed since the 1960s, which is the heritage and the roots of the sport. That’s one of the cool things about NASCAR. We’ve been running these engines for more than 40 years, so what’s different? The materials have gotten better. The lubrication systems have gotten better. The technology in the valvetrain components and the reciprocating components is better. The engineering that’s behind those parts now has allowed that basic 60’s architecture to turn 10,000 RPM and make over 900 horsepower in a 2014 spec. You could not do that with a Boss 429, but you can do it with today’s version of that architecture. So the story is when you look at the performance of the engines today, it’s the same basic architecture from 40 years ago, but we’re making in some cases almost 300 horsepower more, spinning to almost 10,000 RPM and it’s all through engineering, material improvements and really getting the engine to work as a system. Every piece affects something else in the engine and the engineering and analytical tools being used to develop these engines now allow us to make more power than we could before.”

One thing that hasn’t changed is finding the weak links and making them stronger. And as today’s engines get more ‘wrung out,’ every change they make is critical. Simon says, “It’s a never ending loop of finding the limit in one area and then having to open up another area. Take, for example, the crankshaft dynamics. The crankshaft drives the camshaft, so if your crankshaft dynamics get really bad because you’ve done something on the bottom end of the engine, now it throws your valvetrain dynamics off. You can’t touch any part of the engine anymore without affecting the performance of some other part. That’s just where the engines are today. When you look at the throwback of the seventies theme this weekend for Darlington, from an engine perspective we are running a modern day version of that 1970s engine. A lot of people look at that as a negative, but when you consider the development and the engineering that’s gone into taking an old architecture and being able to make 900 horsepower out of a 5.8-liter, it’s really quite impressive. Horsepower per liter-wise, with the Boss 429, they were making approximately 88 horsepower per liter. The 2014 FR9 was 155 horsepower per liter, that’s world-class for a naturally-aspirated engine. The 2015 FR9, with the new engine rules, is still 130 horsepower per liter. You don’t get much better than that. It’s the same basic architecture. It hasn’t changed, so that’s kind of the story.”
THEN AND NOW…COMPARING THE BOSS 429 TO THE FR-9
1970 Boss 429 Engine
Engine: Boss 429 cu. inch V8 with aluminum cylinder heads
Horsepower: 610 @ 7000 rpm
Compression Ratio: 11.5:1
Induction: Holley 4-barrel carburetor
2015 FR-9 Engine
Engine: Cast iron 358 cu. inch V8 with aluminum cylinder heads
Horsepower: 750 @ 9000 rpm
Compression Ratio: 12:1
Induction: McLaren Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI)

The Darlington race brings out a lot of memories for true racers like Yates. From his time as a Championship winning owner back to the days of building those Shotguns, Yates has seen quite a bit. When asked what his fondest memories of Darlington were, we were surprised to find out just how much ‘The Lady in Black’ meant to him on so many levels and through so many years. He started off with his time as a crew member and even talked about his famous carb work, “What I remember so much about Darlington was I used to go there before I was in racing. I’d go with some of my school buddies from East Carolina and we’d go to the Southern 500 and sit under the shade and watch the people go crazy. It was the most fun watching the cars sideways off that corner, so Darlington was one of my favorite tracks. I saw Cale (Yarborough) when he went over the wall. I was actually down on the other end of the track, but many light years later that was the first place I was on a pit crew. I had been nervous the whole time getting ready to gas the car, so a lot of firsts happened for me there, but I always remember the time that Bobby Allison was driving for us. We were so-so, but I figured out something with the carburetor that was legal and when I tried it we were so fast. The Southern 500 was a tough race and a hot race. You had to be good at handling and you had to be good at everything. They dropped the flag and Bobby’s car came off of four and nobody else’s did. I was like, ‘What happened to the field?’ But he was that much further ahead of everybody. The focus Bobby Allison had that day was incredible. That 1972 win, I’ve still got a sticker on my tool box that says Southern 500 Win. Winning the Southern 500 was probably like the Daytona 500.”

Yates went on to talk more about Darlington and how it deeply affected him, “It was always a real fun race. To see those cars come off of four, which is turn two now, was always a lot of fun. Those covered grandstands were very noisy, but I’ve got great memories sitting there. After seeing that I just knew I had to get into this sport because I loved it. That was one of my favorite wins, along with Dale winning there three times. When Dale sat on the pole I said, ‘That is a man’s pole,’ because that was one of the toughest places and that’s something that when we hired Dale, he never sat on a pole anywhere. The first race out with him we sat on the Daytona 500 pole, but Darlington poles are very, very good.”
NASCAR’s rich history lives on. And some of the old engine secrets are coming out of the shadows for fans and racers to enjoy.